Do you need advice? +420 545 235 668
FOREARM AND HAND - DEEP DISSECTION
Catalog number: EM270-MP1514
Product availability: Delivery date HERE
Weight:
3 Kg
Description
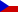
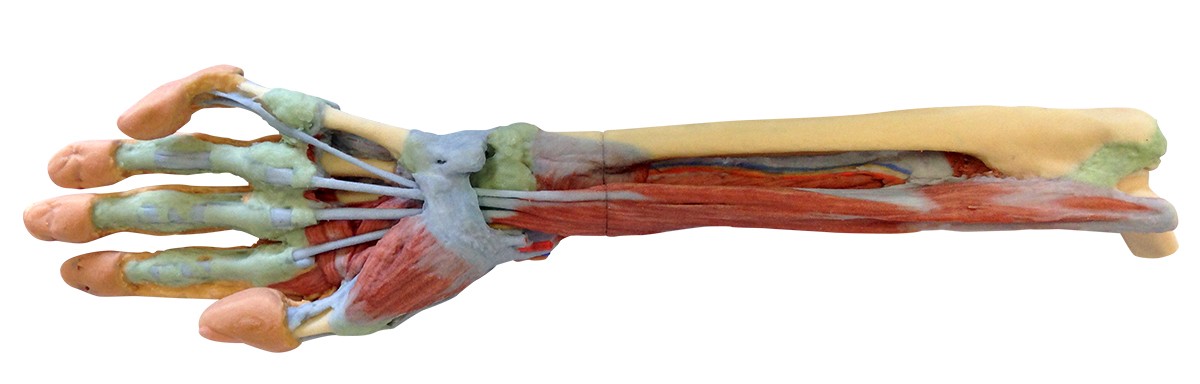
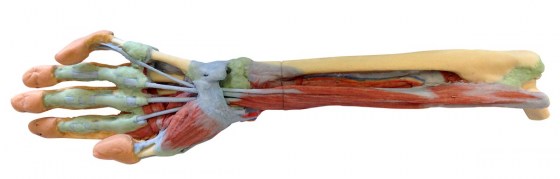
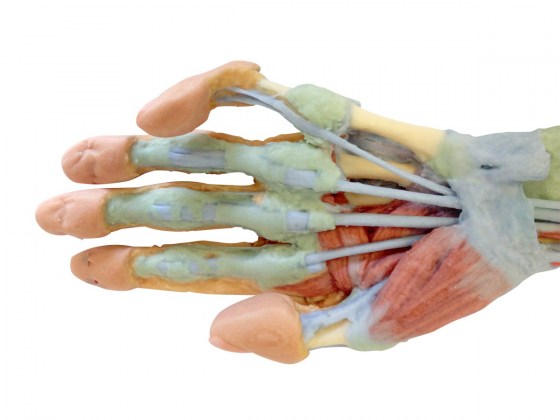
This 3D printed specimen shows a deep dissection of the forearm, from the distal humerus to the palmar surface of hand. This dissection model allows for study of the nerves and muscles.
The 3D Human Anatomy Series is the result of a collaboration between Monash University in Australia and German manufacturer Erler Zimmer. The 3D printed human anatomy models in this collection are highly accurate colour-augmented representations, designed to substitute the use of real human cadavers in anatomy education. Each model has been developed from radiographic data or cadaver specimins, providing a highly cost effective and ethical solution to meet the needs of medical, allied health and biological science educators.
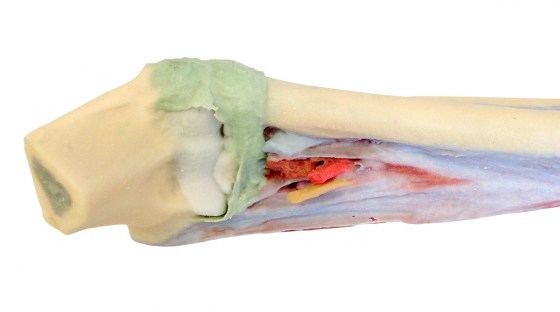
In this deep forearm and hand dissection, the musculature surrounding the distal humerus has been removed except for the humeral origin of the flexor digitorum superficialis from the medial epicondyle. The elbow joint capsule has been dissected and opened anteriorly to demonstrate the articulation of the distal humerus, proximal radius and proximal ulna. The distal portion of the biceps brachii tendon and brachialis muscle is visible in the cubital fossa near the brachial artery, brachial vein, and median nerve. Most of the remaining neurovascular structures and musculature of the forearm have been removed to show the anterior interosseous artery, vein and nerve resting on the interosseous membrane and approaching the pronator quadratus muscle.
With the surrounding musculature dissected the radial origin of the flexor digitorum superficialis is fully exposed, with the distal tendons passing deep to the flexor retinaculum as they pass to the dissected palmar surface of the hand. The distal insertions of the dissected forearm musculature (e.g., brachioradialis, flexor carpi radialis, flexor carpi ulnaris, extensor carpi radialis longus and brevis) and radial artery are visible at the wrist. Within the hand, these tendons pass to their insertions through the fibrous sheaths of the digits (along with the preserved tendons of the flexor digitorum profundus). Laterally the flexor pollicis longus tendon passes to the first digit surrounded by the thenar eminence musculature, while medially the fibrous sheath of the fifth digit has been dissected.
The deep dissection of the hand also demonstrates the transverse and oblique heads of the adductor pollicis, as well as the palmar view of the first dorsal interosseous muscle. The skin on the dorsum of the hand has been largely retained, but has been dissected medially to demonstrate the course of the extensor digitorum and extensor digiti minimi tendons, as well as the extensor expansion.
This 3D printed specimen shows a deep dissection of the forearm, from the distal humerus to the palmar surface of hand. This dissection model allows for study of the nerves and muscles.
The 3D Human Anatomy Series is the result of a collaboration between Monash University in Australia and German manufacturer Erler Zimmer. The 3D printed human anatomy models in this collection are highly accurate colour-augmented representations, designed to substitute the use of real human cadavers in anatomy education. Each model has been developed from radiographic data or cadaver specimins, providing a highly cost effective and ethical solution to meet the needs of medical, allied health and biological science educators.
In this deep forearm and hand dissection, the musculature surrounding the distal humerus has been removed except for the humeral origin of the flexor digitorum superficialis from the medial epicondyle. The elbow joint capsule has been dissected and opened anteriorly to demonstrate the articulation of the distal humerus, proximal radius and proximal ulna. The distal portion of the biceps brachii tendon and brachialis muscle is visible in the cubital fossa near the brachial artery, brachial vein, and median nerve. Most of the remaining neurovascular structures and musculature of the forearm have been removed to show the anterior interosseous artery, vein and nerve resting on the interosseous membrane and approaching the pronator quadratus muscle.
With the surrounding musculature dissected the radial origin of the flexor digitorum superficialis is fully exposed, with the distal tendons passing deep to the flexor retinaculum as they pass to the dissected palmar surface of the hand. The distal insertions of the dissected forearm musculature (e.g., brachioradialis, flexor carpi radialis, flexor carpi ulnaris, extensor carpi radialis longus and brevis) and radial artery are visible at the wrist. Within the hand, these tendons pass to their insertions through the fibrous sheaths of the digits (along with the preserved tendons of the flexor digitorum profundus). Laterally the flexor pollicis longus tendon passes to the first digit surrounded by the thenar eminence musculature, while medially the fibrous sheath of the fifth digit has been dissected.
The deep dissection of the hand also demonstrates the transverse and oblique heads of the adductor pollicis, as well as the palmar view of the first dorsal interosseous muscle. The skin on the dorsum of the hand has been largely retained, but has been dissected medially to demonstrate the course of the extensor digitorum and extensor digiti minimi tendons, as well as the extensor expansion.